Obesity isn’t just about weight—it’s a serious risk factor for multiple chronic conditions across the body. The higher the obesity class (Class I, II, III), the higher the risk.
⚖️ Obesity Classification by BMI
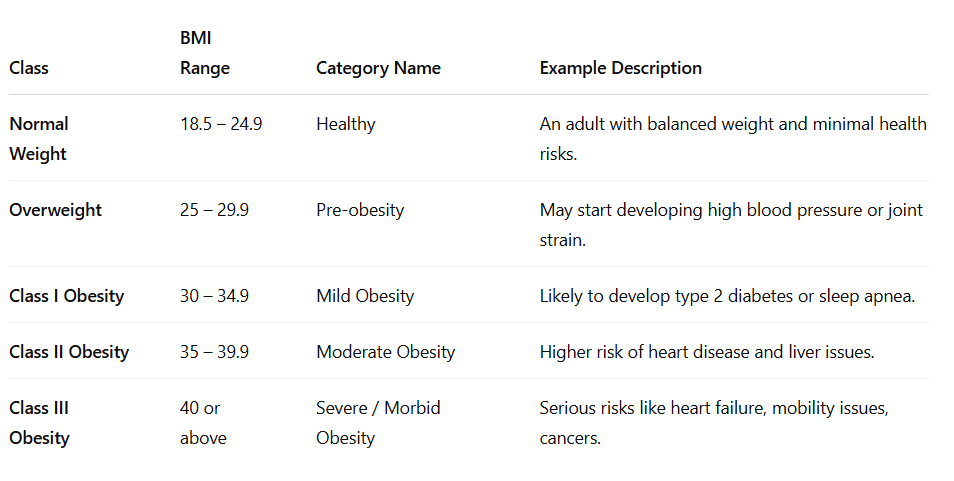
💡 Examples:
- A person with BMI 33 is Class I Obese – may experience fatigue and joint pain.
- A BMI of 37 puts someone in Class II – often accompanied by comorbidities like diabetes.
- BMI 42+ (Class III) – often requires medical/surgical intervention like bariatric surgery.
Below is a summary of the 16 health conditions found to be significantly linked to obesity severity:
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Strongest link observed — people with Class III obesity had nearly 11x higher risk.
- Excess weight narrows the airway and worsens breathing during sleep.
2. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Second-strongest association (hazard ratio ~7.7 for Class III obesity).
- Obesity promotes insulin resistance, a major factor in diabetes development.
3. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- Previously known as NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease).
- Fat accumulation in the liver leads to inflammation and liver damage.
- Risk increases nearly 7-fold in Class III obesity.
4. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Obesity puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, elevating blood pressure.
- Commonly coexists with other cardiometabolic conditions.
5. Hyperlipidemia / Dyslipidemia
- Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels, often driven by obesity-related metabolic dysfunction.
- Increases risk of heart disease and stroke.
6. Heart Failure
- Obesity leads to structural and functional changes in the heart, increasing heart failure risk.
- Often coexists with hypertension and diabetes.
7. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
- Obesity is linked to higher risk of irregular heartbeat, which increases stroke risk.
- Excess fat may lead to atrial enlargement and electrical instability.
8. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD)
- Includes coronary artery disease and heart attacks.
- Fat buildup in arteries worsens with obesity.
9. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Obesity-related high blood pressure and diabetes accelerate kidney damage.
- CKD can progress silently, making screening essential.
10. Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
- Blood clot in the lungs, often life-threatening.
- Obesity increases blood clotting risk and decreases mobility.
11. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Blood clots in deep veins, typically in the legs.
- Risk rises due to impaired circulation and inflammation in obese individuals.
12. Gout
- A painful type of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup.
- Obesity increases uric acid levels and reduces kidney excretion.
13. Biliary Calculus (Gallstones)
- Obesity changes bile composition, promoting gallstone formation.
- Especially common in obese women.
14. Asthma
- Inflammation and reduced lung function more common in individuals with obesity.
- Obesity may worsen asthma symptoms and treatment response.
15. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Extra weight puts pressure on the abdomen, increasing acid reflux.
- Common cause of heartburn, regurgitation, and esophagitis.
16. Osteoarthritis
- Wear and tear on joints (especially knees and hips) due to excess body weight.
- Obesity also increases inflammation, worsening joint pain.
📊 Key Insights:
- 42.4% of participants had obesity; 9.8% had Class III (severe) obesity.
- Risk increased stepwise with higher obesity severity.
- Obesity explained over half of all sleep apnea and over a third of liver disease cases.
- Strong and consistent results across age, sex, and racial groups.
🚨 Why This Matters
This landmark study emphasizes that obesity isn’t just about appearance—it’s a whole-body health risk. From your liver to your lungs, heart to joints, the impact is vast and severe, especially as obesity reaches higher levels.
Effective weight management and public health strategies could prevent a significant proportion of these conditions.
Reference: MedicalXpress



