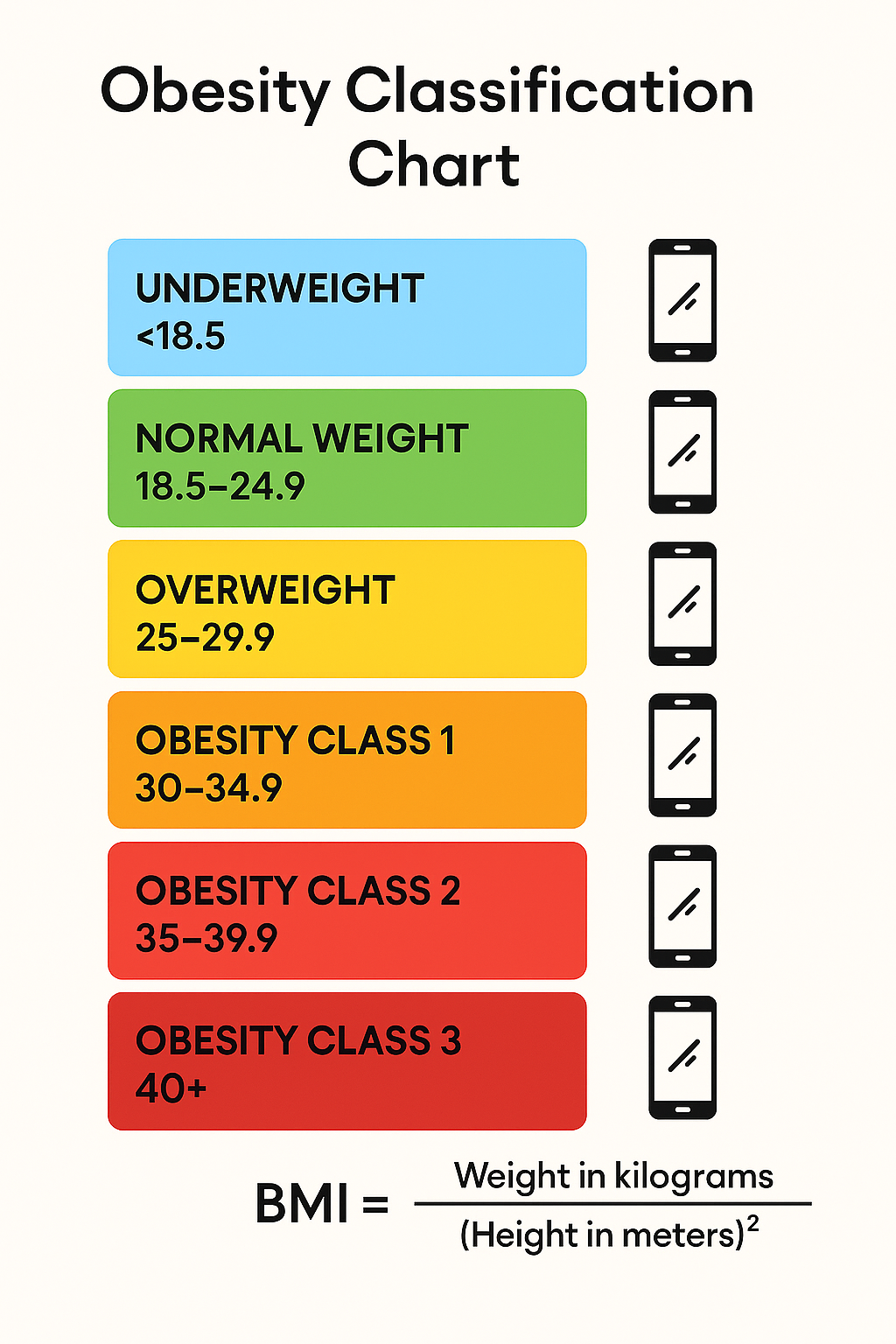
Obesity is classified using Body Mass Index (BMI), a simple weight-to-height ratio that helps assess health risks. Here’s the standard classification:
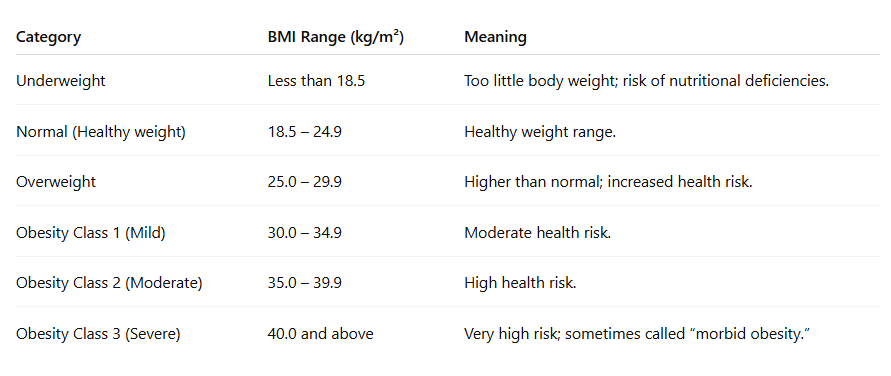
BMI Categories for Adults (WHO Guidelines)
| BMI Range | Classification | Health Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
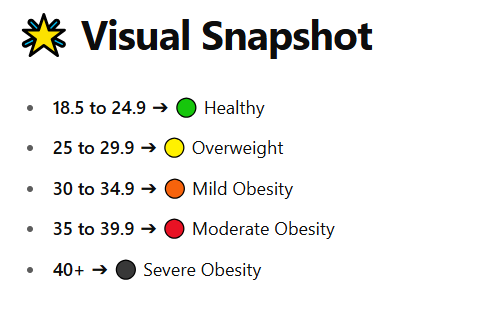
| < 18.5 | Underweight | Increased risk |
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal (Healthy) | Low risk |
| 25–29.9 | Overweight | Moderate risk |
| 30–34.9 | Obesity Class I | High risk |
| 35–39.9 | Obesity Class II | Very high risk |
| ≥ 40 | Obesity Class III (Severe/Morbid) | Extremely high risk |
Key Takeaways:
✔ BMI ≥ 30 = Obesity (increased risk of diabetes, heart disease & more).
✔ BMI ≥ 40 = Severe obesity (may qualify for weight-loss surgery).
✔ BMI is a screening tool—not a complete health measure (muscle mass, waist size, and genetics also matter).
Next Steps: If your BMI falls in the overweight or obesity range, consult a doctor for personalized advice on diet, exercise, or medical treatments (like GLP-1 medications).
Obesity Classification Chart
Important Notes:
- BMI is a useful general guide but doesn’t account for muscle mass, bone density, or distribution of fat.
- Waist circumference and body fat percentage are additional tools doctors use for a full health assessment.
- Children and teens have different BMI charts based on age and sex.